What is AFC?
AFC is focused on the design, development, and qualification of advanced nuclear fuels and materials that can significantly improve the performance, safety, and efficiency of current and future nuclear reactors. The campaign’s efforts encompass a variety of advanced nuclear fuel concepts, including Accident Tolerant Fuels (ATF), tri-structural isotropic (TRISO)-coated particle fuels, molten salt fuels, and metallic fuels.
The work conducted by the AFC is crucial for enhancing the overall safety and robustness of nuclear reactors, particularly in the event of accidents or extreme conditions. Furthermore, these advanced fuels aim to extend the operational life of nuclear fuel, reduce the amount of nuclear waste generated, and support the United States’ strategic energy objectives by fostering innovation in nuclear technology.

Mission
Vision
Values
Safety
We prioritize the utmost safety in all our research and development activities, ensuring that every innovation adheres to the highest safety standards to protect both the industry and the public.
Stewardship
Reliability
Innovation
We are dedicated to continuous innovation, adapting and refining technology to meet and exceed the evolving challenges of nuclear fuel performance.
Excellence
How We Got Here
Research and Development Areas
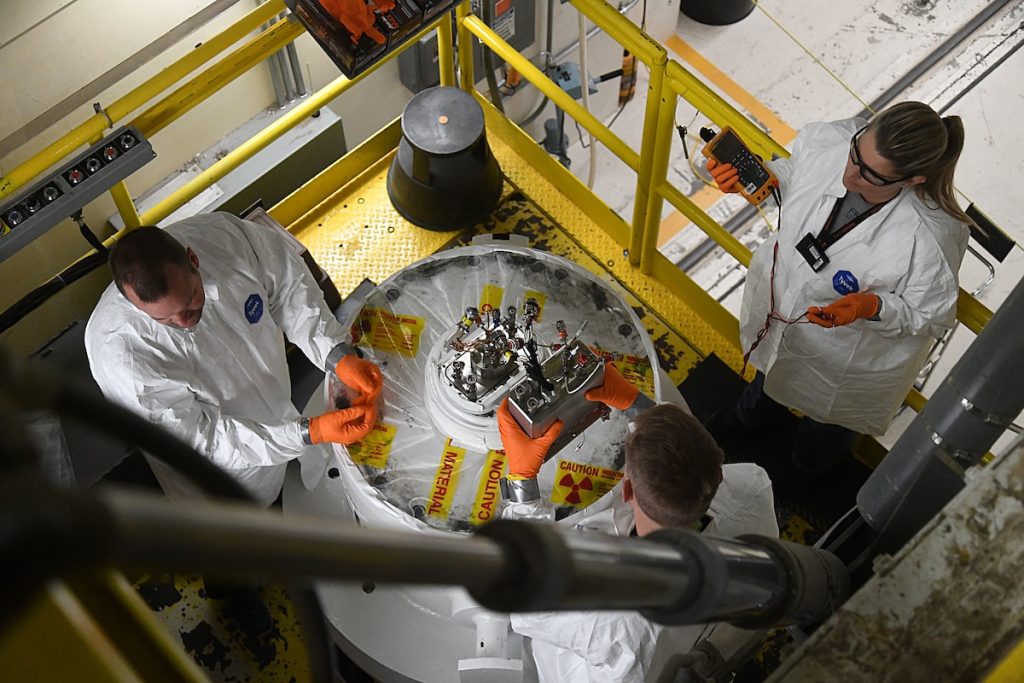
AFC focuses on key research and development topics, such as enhancing Accident Tolerant Fuel (ATF), perfecting tri-structural isotropic (TRISO) coated particle fuel, and furthering the development of metallic fuels and molten salt fuels. These critical undertakings are fundamental to the AFC’s commitment to improving the safety, operational efficiency, and eco-friendliness of nuclear energy systems.
Molten salt fuels contain fissile materials such as uranium, thorium or plutonium. These fuels are chemically stably at high temperatures and have a high boiling point. Fuel salts flow and circulate throughout the reactor, enhancing heat transfer and potentially improving reactor efficiency. The radiation performance of the fuel salt is primarily influenced by its chemical stability and off-gassing. Since the fuel is in a liquid state, long-term defect accumulation and structural changes are less of a concern compared to solid fuel types.
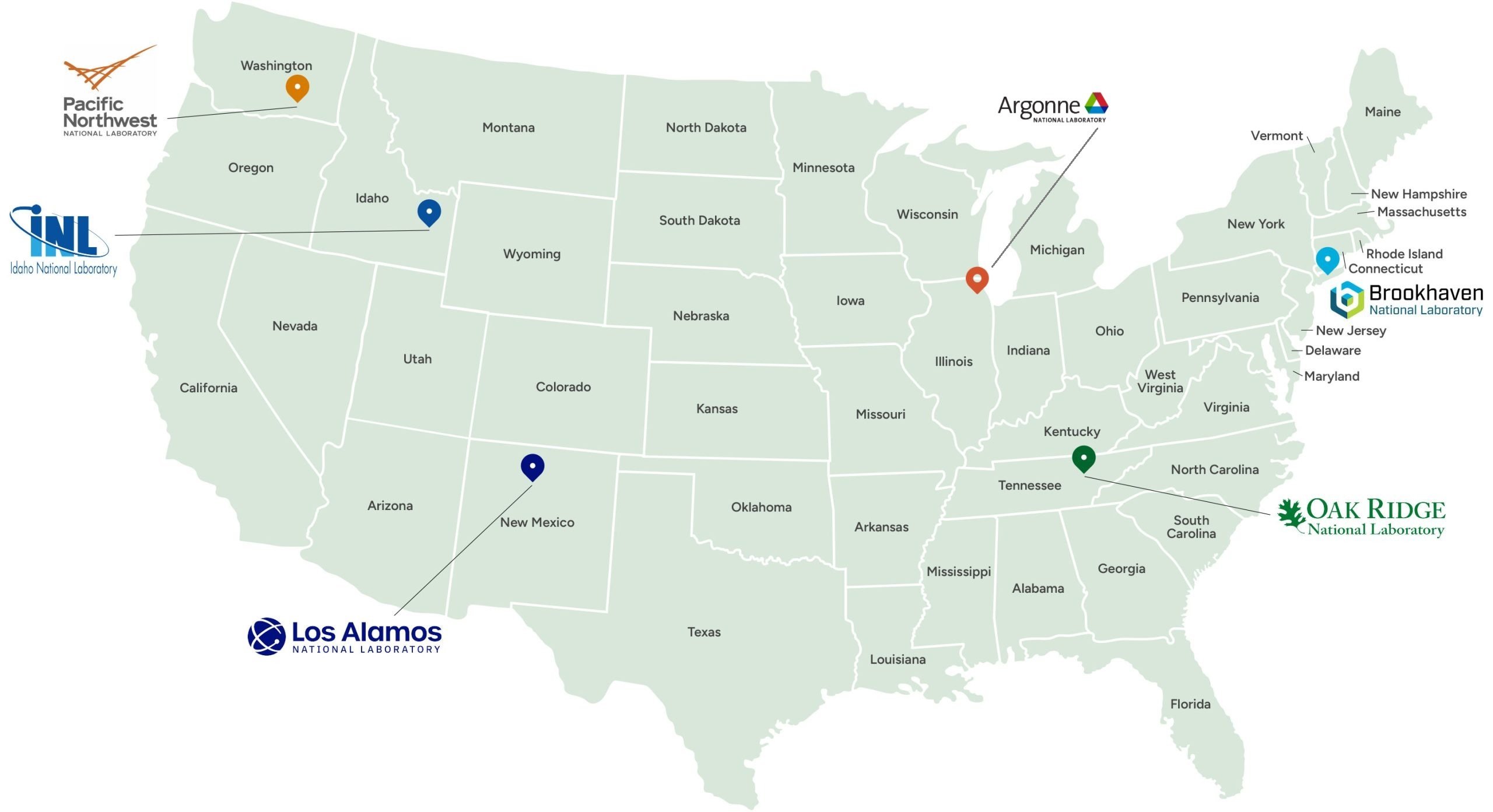
AFC Laboratories
The Advanced Fuels Campaign is a collaborative effort involving teams from Idaho National Laboratory, Oak Ridge National Laboratory, Los Alamos National Laboratory, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory, Brookhaven National Laboratory, and Argonne National Laboratory.